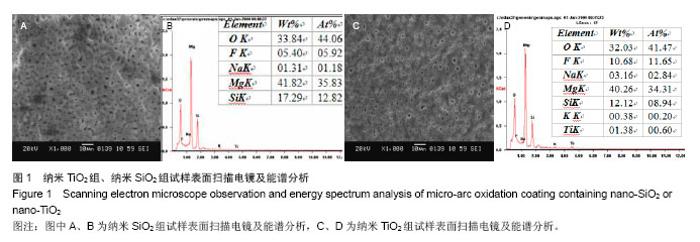
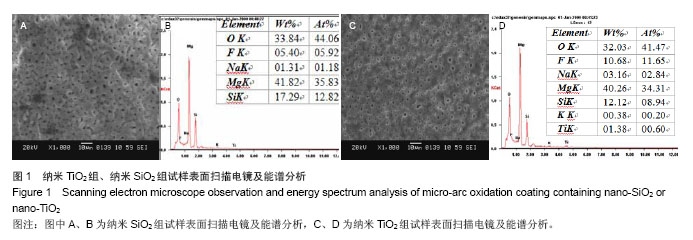
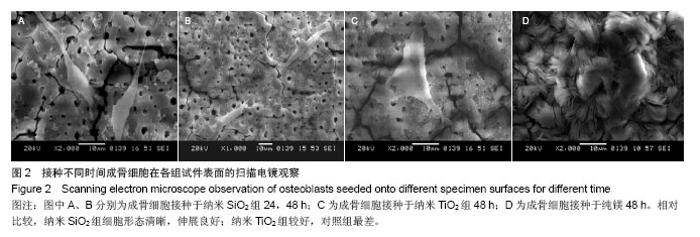
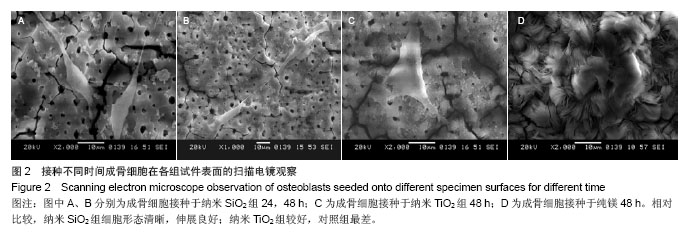
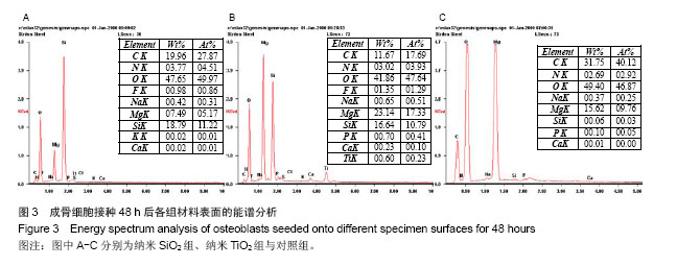
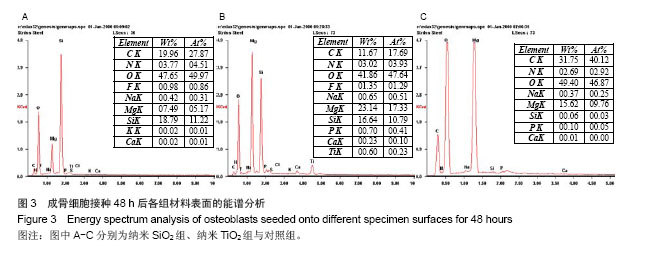
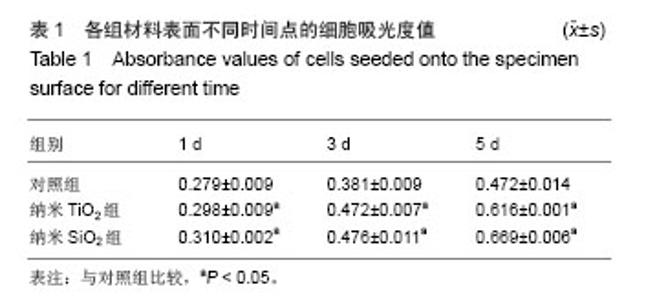
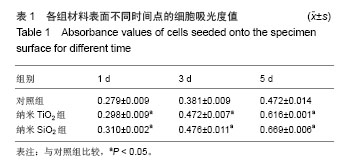
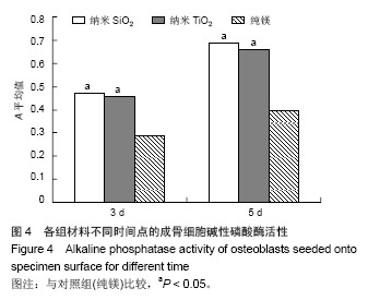
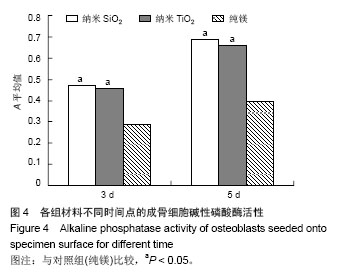
| [1]Witte F,Kaese V,Haferkamp H, et al. In vivocorrosion of four magnesium alloys and the associated bone response.Biomaterials. 2005;26(17):3557-3563.
[2]袁广银,章晓波,牛佳林,等.新型可降解生物医用镁合金JDBM的研究进展[J].中国有色金属学报,2011,23(10):2476-2488.
[3]黄晶晶,任伊宾,张炳春,等.镁及镁合金的生物相容性研究[J].稀有金属材料与工程,2007,36(6):1102.
[4]Liang J,Hu L,Hao JC.Improvement of corrosion properties of micro-arc oxidation coating on magnesium alloy by optimizing current den-sity parameters. Applied Surface Science.2007; 253(16):6939-6945.
[5]祝晓文,韩建民,崔世海,等.铝、镁合金微弧氧化技术研究进展[J].材料科学与工艺, 2006, 14(3):366-369.
[6]蒋百灵,张淑芬,吴国建,等.镁合金微弧氧化陶瓷层纤维缺陷与相组成及耐蚀性[J].中国有色金属学报,2002,12(3):454-457.
[7]郝建民,陈宏,张荣军,等.镁合金微弧氧化陶瓷层的耐蚀性[J].中国有色金属学报,2003,13(4):988-991.
[8]胡文祥,桑宝华,谭生建,等.分子纳米技术在生物医药学领域的应用[J].化学通报,1998,21(2):32-38.
[9]周承调.纳米技术的进展和医用纳米生物材料[J].大连大学学报, 2001,22(6):3-5.
[10]蔡开勇.纳米生物材料及其界面特性对成骨细胞生长影响的研究进展[J].材料导报, 2007,21(2):109-124.
[11]张林,庞小峰.纳米二氧化钛的细胞增殖效应及其安全性[J].生命科学仪器,2007,5(7): 54-56.
[12]Ni S,Chou L,Chang J.Preparation and characterization of forsterite(Mg2SiO4) bioceramics.Ceram Inter.2007;33:83-88.
[13]Morton D,Jaffin R,Weber HP,et al.Immediate restoration and loading of dental implants: clinical considerations and protocols. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2004;19:103-108.
[14]Anselme K,Bigerelle M,Noel B,et al.Effect of grooved titanium substratum on human osteoblastic cell growth.J Biomed Mater Res.2002;60(4):529.
[15]Webster TJ,Ergun C,Doremus RH,et al.Specific pro-teins mediate enhanced osteoblast adhesion on nanophase ce-ramics.J Biomed Mater Res.2000;51(3):475. |